Overview
 Morton’s Neuroma is a common problem in runners, and there are a number of simple fixes you can try before resorting more drastic solutions like sclerosing or surgery. A Morton’s Neuroma normally causes a burning pain in the forefoot, just behind the 3rd and 4th toes (sometimes behind the 2nd and 3rd toes). The pain often radiates towards the toes, and sometimes there is numbness rather than pain. The underlying cause is inflammation of the nerve between the bones of the forefoot, often triggered by narrow or tight shoes. I have had good results with the simple fixes described below, and I have had reports of other runners with similar success.
Morton’s Neuroma is a common problem in runners, and there are a number of simple fixes you can try before resorting more drastic solutions like sclerosing or surgery. A Morton’s Neuroma normally causes a burning pain in the forefoot, just behind the 3rd and 4th toes (sometimes behind the 2nd and 3rd toes). The pain often radiates towards the toes, and sometimes there is numbness rather than pain. The underlying cause is inflammation of the nerve between the bones of the forefoot, often triggered by narrow or tight shoes. I have had good results with the simple fixes described below, and I have had reports of other runners with similar success.
Causes
Anything that causes compression or irritation of the nerve can lead to the development of a neuroma. One of the most common causes comes from wearing shoes that have a tapered toe box, or high-heeled shoes that cause the toes to be forced into the toe box and overload pressure onto the forefoot. An injury or trauma to the forefoot may also lead to a neuroma. People at a higher risk of developing a Neuroma include people with certain foot deformities, such as bunions or hammertoes. Certain foot types, such as flat feet (Pronation) More flexible feet, and woman after pregnancy.
Symptoms
Feelings of numbness, tingling or tenderness in the ball of the foot (the area just behind the base of the toes) are some of the first signs of a condition known as Morton?s Neuroma. However, the condition is somewhat unpredictable, and symptoms may vary from patient to patient. Generally, however, the discomfort gets worse rather than better, and the patient may feel pain or a burning sensation that radiates out to the toes. Eventually, wearing shoes becomes uncomfortable (or even unbearable), and the patient may complain that the feeling is similar to that of having a stone bruise, or walking on a marble or pebble constantly, even though no there is no trauma to the skin, and no visible bump or lump on the sole of the foot.
Diagnosis
The doctor will perform an examination of your feet as well. He or she may palpate your feet and flex them in specific ways that will indicate the presence of a neuroma. X-rays are often used to rule out other problems, such as fractures, bone spurs, arthritis or other problems with the bones in the toes or foot. In some cases, an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) may be helpful to confirm the presence of a neuroma.
Non Surgical Treatment
Wear shoes with plenty of room for the toes to move, low heels, and laces or buckles that allow for width adjustment. Wear shoes with thick, shock-absorbent soles, as well as proper insoles that are designed to keep excessive pressure off of the foot. High-heeled shoes over two inches tall should be avoided whenever possible because they place undue strain on the forefoot. Resting the foot and massaging the affected area can temporarily alleviate neuroma pain. Use an ice pack to help to dull the pain and improve comfort. Use over-the-counter shoe pads. These pads can relieve pressure around the affected area.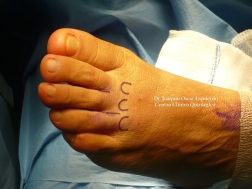
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment does not relieve your symptoms, your orthopaedic surgeon may discuss surgical treatment options with you. Surgery can resect a small portion of the nerve or release the tissue around the nerve, and generally involves a short recovery period.






 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms



 Achilles tendinitis is an irritation/inflammation in the achilles tendon, which attaches to the back of the heel. It is often a result of overuse and occurs frequently in runners who have altered their training suddenly, either with regard to duration or intensity. This injury is also prevalent in middle-aged people who are active.
Achilles tendinitis is an irritation/inflammation in the achilles tendon, which attaches to the back of the heel. It is often a result of overuse and occurs frequently in runners who have altered their training suddenly, either with regard to duration or intensity. This injury is also prevalent in middle-aged people who are active.
You must be logged in to post a comment.